We are covering here -'Java garbage collection interview questions' or 'Java memory interview questions' in details. The topic is always asked to senior java developers to verify the java memory model understanding. In bigger project taking care of VM memory becomes very important due to more memory required at peak time processing in application.
In this topic frequently asked questions are:
- What is Garbage collection?
- How to do analysis of java memory issues?
- Explain Java memory model?
- What are garbage collectors?
- How to use java profilers?
- Have you worked in application performance improvement?
- What are the memory issues you have faced in your application?
Garbage Collection:
Garbage collection (GC) is a form of automatic memory management. The garbage collector, or just collector, attempts to reclaim garbage, or memory occupied by objects that are no longer in use by the program. Garbage collection was invented by John McCarthy around 1959 to solve problems in Lisp.
 Garbage collection is often portrayed as the opposite of manual memory management, which requires the programmer to specify which objects to deallocate and return to the memory system. However, many systems use a combination of approaches, including other techniques such as stack allocation and region inference.
Garbage collection is often portrayed as the opposite of manual memory management, which requires the programmer to specify which objects to deallocate and return to the memory system. However, many systems use a combination of approaches, including other techniques such as stack allocation and region inference.Resources other than memory, such as network sockets, database handles, user interaction windows, and file and device descriptors, are not typically handled by garbage collection. Methods used to manage such resources, particularly destructors, may suffice to manage memory as well, leaving no need for GC. Some GC systems allow such other resources to be associated with a region of memory that, when collected, causes the other resource to be reclaimed; this is called finalization. Finalization may introduce complications limiting its usability, such as intolerable latency between disuse and reclaim of especially limited resources, or a lack of control over which thread performs the work of reclaiming.
Memory is divided in mainly 3 areas:
- Young\Eden Generation : for newly created objects.
- Tenured Generation : for old objects which are survived after minor gc.
- Perm Space : for class definition, meta data and string pools.
At initialization, a maximum address space is virtually reserved but not allocated to physical memory unless it is needed. The complete address space reserved for object memory can be divided into the young and tenured generations.The young generation consists of eden and two survivor spaces. Most objects are initially allocated in eden. One survivor space is empty at any time, and serves as the destination of any live objects in eden and the other survivor space during the next copying collection. Objects are copied between survivor spaces in this way until they are old enough to be tenured (copied to the tenured generation). A third generation closely related to the tenured generation is the permanent generation which holds data needed by the virtual machine to describe objects that do not have an equivalence at the Java language level.
Java objects are created in Heap and Heap is divided into three parts or generations of garbage collection in Java as mentioned above. New Generation is divided into three parts known as
- Eden space
- Survivor 1
- Survivor 2 space.
When an object first created in heap its gets created in new generation inside Eden space and after subsequent Minor Garbage collection if object survives its gets moved to survivor 1 and then Survivor 2 before Major Garbage collection moved that object to Old or tenured generation.
Permanent generation of Heap or Perm Area of Heap is special and it is used to stores String pool, Meta data related to classes and method in JVM.
Permanent generation of Heap or Perm Area of Heap is special and it is used to stores String pool, Meta data related to classes and method in JVM.
Out Of Memory / OOM :
If it happens in your application take it is opportunity to display your technical skills. In technical term it means the JVM does not have space to put objects in tenured space which are survived in minor collection and it stops working or responding due to no memory to do further processing.
- Throughput is the percentage of total time not spent in garbage collection, considered over long periods of time. Throughput includes time spent in allocation (but tuning for speed of allocation is generally not needed).
- Pauses are the times when an application appears unresponsive because garbage collection is occurring.
- Footprint is the working set of a process, measured in pages and cache lines. On systems with limited physical memory or many processes, footprint may dictate scalability.
- Promptness is the time between when an object becomes dead and when the memory becomes available, an important consideration for distributed systems, including remote method invocation (RMI).
- Heap Dump is a list of objects in the memory of JVM as well as the content of the memory occupied by those objects. It preserves the value of any attributes of the objects, including references to other objects. In other words, a heap dump gives you a complete picture of the memory.There are multiple tools that allow you to dump heap in a Java process:Some tools like VisualVM and memory profilers allow you to initiate a heap dump from the GUI, but you don’t need any fancy tools here—jmap will do just fine. As it provides the most general case, we'll use jmap in the next example.Before you dump heap, be sure to keep the following issues in mind:Note that the -F option, which will dump non-responsive programs, might be useful on UNIX systems, but is not available on Windows. Note also that JDK 6 includes the option +XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError that will dump heap whenever the OutOfMemoryError alert is encountered. This can be a useful option, but keep in mind that it has the potential to consume significant amounts of disk space.
The basic principles of garbage collection are:
- Find data objects in a program that cannot be accessed in the future
- Reclaim the resources used by those objects
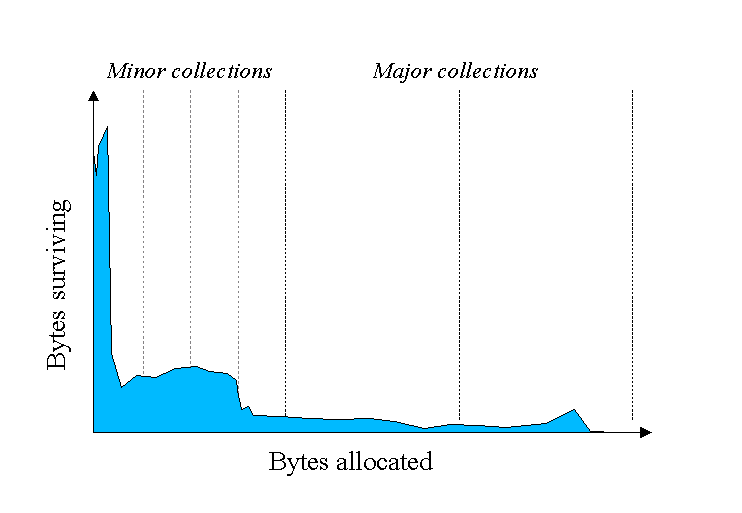
An object is considered garbage when it can no longer be reached from any pointer in the running program. The most straightforward garbage collection algorithms simply iterate over every reachable object. Any objects left over are then considered garbage. The time this approach takes is proportional to the number of live objects, which is prohibitive for large applications maintaining lots of live data.The blue area in the diagram below is a typical distribution for the lifetimes of objects. The X axis is object lifetimes measured in bytes allocated. The byte count on the Y axis is the total bytes in objects with the corresponding lifetime. The sharp peak at the left represents objects that can be reclaimed (i.e., have "died") shortly after being allocated. Iterator objects, for example, are often alive for the duration of a single loop.
Application GC bytes allocation is shown in above picture. Majority of byte survival happens in Minor Collection and majority of objects are cleared in Major collections. Some objects do live longer, and so the distribution stretches out to the the right. For instance, there are typically some objects allocated at initialisation that live until the process exits. Between these two extremes are objects that live for the duration of some intermediate computation, seen here as the lump to the right of the initial peak. Some applications have very different looking distributions, but a surprisingly large number possess this general shape. Efficient collection is made possible by focusing on the fact that a majority of objects "die young".
Collectors
The Java HotSpot VM includes three different collectors, each with different performance characteristics.
- The serial collector uses a single thread to perform all garbage collection work, which makes it relatively efficient since there is no communication overhead between threads. It is best-suited to single processor machines, since it cannot take advantage of multiprocessor hardware, although it can be useful on multiprocessors for applications with small data sets (up to approximately 100MB). The serial collector is selected by default on certain hardware and operating system configurations, or can be explicitly enabled with the option -XX:+UseSerialGC.
- The parallel collector (also known as the throughput collector) performs minor collections in parallel, which can significantly reduce garbage collection overhead. It is intended for applications with medium- to large-sized data sets that are run on multiprocessor or multi-threaded hardware. The parallel collector is selected by default on certain hardware and operating system configurations, or can be explicitly enabled with the option -XX:+UseParallelGC.
- New: parallel compaction is a feature introduced in J2SE 5.0 update 6 and enhanced in Java SE 6 that allows the parallel collector to perform major collections in parallel. Without parallel compaction, major collections are performed using a single thread, which can significantly limit scalability. Parallel compaction is enabled by adding the option -XX:+UseParallelOldGC to the command line.
- The concurrent collector performs most of its work concurrently (i.e., while the application is still running) to keep garbage collection pauses short. It is designed for applications with medium- to large-sized data sets for which response time is more important than overall throughput, since the techniques used to minimize pauses can reduce application performance. The concurrent collector is enabled with the option -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC.
VM Options for GC details:
- -verbose:gc — prints basic information about GC to the standard output
- -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps — prints the times that GC executes
- -XX:+PrintGCDetails — prints statistics about different regions of memory in the JVM
- -Xloggc: — logs the results of GC in the given file.
- -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote — enables JMX monitoring
- -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port = — controls the port for JMX monitoring
- com.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl
- com.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate
- If you're using JDK 6, you can use tool called jmap on any platform.
What is Garbage First Collector?
Recently in one java interview, I was asked about Garbage First collector and Garbage First collector splits the heap up into fixed-size regions and tracks the live data in those regions. It keeps a set of pointers — the "remembered set" — into and out of the region. When a GC is deemed necessary, it collects the regions with less live data first (hence, "garbage first"). Often, this can mean collecting an entire region in one step: if the number of pointers into a region is zero, then it doesn't need to do a mark or sweep of that region.Technical description
The G1 collector achieves high performance and pause time goals through several techniques.
The heap is partitioned into a set of equal-sized heap regions, each a contiguous range of virtual memory. G1 performs a concurrent global marking phase to determine the liveness of objects throughout the heap. After the mark phase completes, G1 knows which regions are mostly empty. It collects in these regions first, which usually yields a large amount of free space. This is why this method of garbage collection is called Garbage-First. As the name suggests, G1 concentrates its collection and compaction activity on the areas of the heap that are likely to be full of reclaimable objects, that is, garbage. G1 uses a pause prediction model to meet a user-defined pause time target and selects the number of regions to collect based on the specified pause time target.
The regions identified by G1 as ripe for reclamation are garbage collected using evacuation. G1 copies objects from one or more regions of the heap to a single region on the heap, and in the process both compacts and frees up memory. This evacuation is performed in parallel on multi-processors, to decrease pause times and increase throughput. Thus, with each garbage collection, G1 continuously works to reduce fragmentation, working within the user defined pause times. This is beyond the capability of both the previous methods. CMS (Concurrent Mark Sweep ) garbage collection does not do compaction. ParallelOld garbage collection performs only whole-heap compaction, which results in considerable pause times.
It is important to note that G1 is not a real-time collector. It meets the set pause time target with high probability but not absolute certainty. Based on data from previous collections, G1 does an estimate of how many regions can be collected within the user specified target time. Thus, the collector has a reasonably accurate model of the cost of collecting the regions, and it uses this model to determine which and how many regions to collect while staying within the pause time target.
Recommended Use Cases for G1
The first focus of G1 is to provide a solution for users running applications that require large heaps with limited GC latency. This means heap sizes of around 6GB or larger, and stable and predictable pause time below 0.5 seconds.
Applications running today with either the CMS or the ParallelOld garbage collector would benefit switching to G1 if the application has one or more of the following traits.
- More than 50% of the Java heap is occupied with live data.
- The rate of object allocation rate or promotion varies significantly.
- Undesired long garbage collection or compaction pauses (longer than 0.5 to 1 second)